
When you’re playing poker, it’s assumed that taking risks is the guarantee to cash in large sums of money. Things don’t exactly work the same way with cryptocurrency transactions. In fact, we recommend you take the security of your cryptocurrencies and crypto wallet seriously. After all, they say the difference between SpaceX and Bitcoin is that SpaceX will actually return to earth after takeoff. If someone grabs the keys of your crypto wallet, you can wave your digital money goodbye because they’ll be gone forever.
Let’s dig deeper into the world of crypto wallets and find out the security vulnerabilities you should be looking out, so you can keep the contents of your crypto wallet intact.
The Security Risks of Crypto Wallets
Before delving into the security part, here’s what you need to know about how crypto wallets work:
- when you create any type of wallet, you’ll receive a “seed phrase” – a combination of 12 words (or 15 words, or 24 words) long
- this seed phrase lets you generate the private keys or password
- private keys then generate corresponding public keys that allow you to receive cryptocurrency transactions
Losing your seed phrase means losing access to your wallet, while losing the private keys means losing your crypto funds. That said, it’s important to keep them safe, especially since cybercriminals will keep exploiting any weak point. And sometimes, the weakest point is not knowing how to spot or deal with these wallets’ security risks.
Any digital asset is vulnerable to online attacks, and cryptocurrencies and anything related to them have faced many. Just take a look at the recent statistics showing cryptocurrency lost to and recovered from theft between March 2020 and February 2022:
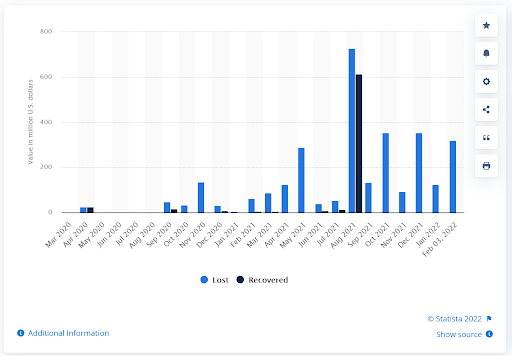
Source: Statista
The most common risks of crypto wallets include:
- Redirecting tokens – by using the trick of inserting a different token, someone can capture your crypto transfers and send them to another wallet.
- Hacking access keys – cybercriminals can grab your access keys by exploiting various vulnerabilities like code errors.
- Social engineering attacks – successful phishing attacks targeting either the wallet or the wallet owner can lead to grabbing access key or password information, so attackers can easily get inside crypto wallets.
- Cyber-attacks – some successful attacks were precursors of data breaches or successful phishing campaigns where cyber-crooks brute forced user passwords, stole wallet user PINs, hacked key storage.
Regardless of the type of attack, they all rely on your poor attention to detail or the unfortunate situation where you’ll make an error. Still, you can minimize the possibilities of human errors if you choose a safe crypto wallet.
Hot Wallet vs. Cold Wallet – Which One to Choose?
There’s a wide array of crypto wallets, and choosing the right one makes all the difference from a security point of view. You’ve heard about hot, cold, custodial, or non-custodial wallets. Check the details of what each of them entails.
Custodial or Non-custodial Wallets
A custodial wallet means you allow a company (one example would be Coinbase) to create a blockchain account on your behalf and let that company manage your keys. This makes that company the custodian of your account, one advantage being that you can recover your keys if you lose them.
With non-custodial wallets, you’ll be the sole and unique manager of your public and private keys. With complete control comes great responsibility, meaning you can’t rely on anyone else but yourself for the safe storage of the keys.
Hot Wallet
Everyone likes the ease of use and simple setup, which is why hot (software) wallets are utterly popular. When creating an exchange account, all you have to do is download a desktop or mobile wallet and ta-da! You got yourself a hot wallet.
Hot wallets are particularly convenient if you’re an active trader and frequently engage in crypto exchanges. The trade-off to ease of use is poor security, though. Hot wallets are always online, so security experts labeled them unsafe and prone to attacks.

*Tip: Don’t keep big amounts of crypto in a hot wallet! The idea that having too much physical cash on you poses a high risk of losing them applies to hot wallets. The reason is fairly simple: you’ll never recover what you lose if you’re a victim of crypto theft.
Cold Wallet
Unlike the hot ones, cold crypto wallets aren’t stored online. There are two types of cold wallets:
- Hardware wallets – usually a USB stick that stores the private key.
- Paper wallets – a piece of paper that cover a public wallet address and a private key.
Cryptocurrency transactions still happen online, but only when you connect your cold wallet on the internet. For instance, you can store crypto in your hardware wallet if you send it from a hot wallet to your hardware wallet’s public address.
Security-wise, cold wallets are pretty close to the definition of unbreakable. Nothing is 100% hackproof, but cold wallets were designed to keep your private keys out of anyone’s sight. You perform the final step of signing the transactions “in-device,” and only then share it to the network. Your device (e.g. the USB-like stick) is the only one that stores the private key.

When it comes to safety, hardware or cold wallets lead the top. Also, security experts believe it’s best not to have any middlemen between you and your crypto wallet, so non-custodial would be a wise choice.
Security Glitches of Crypto Wallet Apps
Not all crypto wallet platforms are built the same way and sadly, some of them aren’t designed, with security in mind.
Low Protection on User Authentication and Data Storage
In some cases, poor security starts from the very beginning – the authentication step. Some crypto wallet apps don’t enforce a strong password policy or don’t provide options for additional authentication steps like biometrics verification (e.g., enable access to data via Keychain/Keystore) or other security controls. Lack of these controls makes your crypto wallet a low-hanging fruit that attackers can swiftly grab.
As far as data storage, they can cover flaws like:
- It’s easily accessible as a file or by other apps.
- Some don’t cover authorization checks, meaning anyone has access and can change stored data.
- While it should come by default, some data storage isn’t encrypted.
These are fine security details you can’t always check to see if they happen. Still, some crypto wallets provide significant information on their websites, like:
- How they store sensitive data on servers disconnected entirely from the internet.
- If they use encrypted cloud storage.
- If they keep drives and paper backups in safe deposit boxes and vaults.
Mobile Platform Security Issues
Crypto wallet mobile applications often don’t perform a thorough check of the device. It’s extremely important that the smartphone doesn’t have any malicious apps installed. Mobile malware can lead to stealing users’ credentials or private keys. Sometimes you may become a collateral victim even if your phone is in perfect shape.
One real example was with the Bitcoin wallet Android application in 2015. A flaw in the app led to several different users having the same wallet. As a result, the bug generated one address multiple times, and all the users of the same wallet lost their funds.
Poor Security of Cryptographic Keys
Non-custodial wallets manage many cryptographic operations; they perform funds encryption, sign transactions, and communicate with decentralized apps through secure protocols.
Sometimes cryptographic code suffers from design flaws and implementation errors. As many non-custodial crypto wallets are open-source, snooping eyes can quickly identify and exploit cryptographic issues. Among several flaws, here’s what security experts saw in many crypto wallets code:
- Poor key management (storing encryption keys in plaintext together with data; using the same set of cryptographic keys for several different purposes).
- Poor memory management of secrets (keeping sensitive data exposed and unsecured in the application code).
- Storing wallet’s sensitive data in plaintext.
This comes to show that crypto wallets and tight security don’t make a good pair for the moment. But there are a few things you can do to overcome threats related to your crypto wallet.
8 Final Tips on Protecting Your Crypto Wallet
You have now seen some of the most common vulnerabilities and pitfalls of crypto wallets. The next step is to ensure you fend off any security risk to avoid having your cryptocurrencies stolen. It all goes down to enforcing a few safety habits, like:
1. Use a strong password for your wallet
The rule of thumb with strong passwords is a combination of lowercase and uppercase letters, numbers and symbols, and the longer the better! To make your life easier, rely on a password manager that’ll help you automatically generate strong passwords for each of your online accounts. In addition to a strong password, MFA as an extra security step is always a good choice.
2. Don’t store your seed phrase online
It may sound like going back to the pre-internet era, but all the victims who dealt with cryptocurrency scams give the same advice: don’t digitize your seed phrase! Even if you save it as an image, in the cloud, or encrypt it, it’s best that you simply write it in a notebook using pen and paper. Also, you can consider products like CryptoSteel, where you can use alphabetical letters embedded in stainless steel, making sure nothing can damage your seed phrase stored on paper.
3. Don’t share your seed phrase or private key
Your private keys equal the keys to your kingdom, so you should always cautiously guard them. Store them in a safe place, and preferably, don’t share them with anyone. If you decide to share the keys, don’t do it in an email, SMS text or any online medium. The best option is to print it on paper or write it down and destroy any trace afterward.
4. Always use a secure internet connection
As Wi-Fi networks are everywhere, they’ve become attackers’ honey pot. First off, avoid public Wi-Fi networks altogether! Most of them aren’t properly secured, and snoopers can easily see all your online traffic, including the content of your crypto wallet and cryptocurrency transactions. Always use a VPN to stay safe on open hotspots. As for your home network, create your own, unique, strong Wi-Fi password and take the time to configure it by choosing advanced security settings.
5. Beware the risks of provider-hosted wallets
Some crypto wallets are hosted by a third-party (usually an exchange company) that manages your wallet, providing custody and other services, including theft protection. Like a bank, you instruct this exchange company about what you want it to do with your cryptocurrencies. It sounds like a hassle-free business, but here’s the downside: you basically allow storage of your private key on this company’s servers. You risk exposing your private keys to anyone who has access to those servers.
6. Keep your software up to date
Most software updates come with security patches that will prevent malicious actors from exploiting potential vulnerabilities. That’s why it’s crucial that you don’t miss any update notification for your crypto wallet software. You’ll not only keep it safe, but some updates even include new useful features.
7. Choose multi-signature feature
Some crypto wallets such as the ones from Bitcoin cover a multi-signature feature, meaning a transaction needs several approvals before it’s complete. This allows you to be more in control over your money and avoid having your funds stolen. Or use a multisignature wallet based on a smart contract such as the ones used to secure ethereum that work on the same rule: requiring multiple parties to agree on transactions before execution. Similar to the principle of a business bank account, a transaction is executed only when it’s confirmed by a predefined number of authorized members.
8. Back up your digital wallet
If you’re in the habit of backing up your data, you can easily understand why backing up your crypto wallet is vital too. Choose different and safe locations for your backup (CD, USB drive, paper, encrypted cloud, etc.) For online backups, you can choose encryption tools like GnuPG or VeraCrypt. You can move the funds to another wallet as an extra precautionary measure.
Bottom Line – The Security of Your Wallet Is in Your Hands
The cryptocurrency industry is evolving and constantly upgrading to safer measures and more secure settings. Still, you shouldn’t rely on them 100% and try to stay ahead of the game. No one will protect your crypto wallet better than you, so keep all the advice above in mind and keep your crypto wallet safe!

 Solving Ethernaut Level 29: Switch
Solving Ethernaut Level 29: Switch  How to Double-Check Smart Contract State Changes with Hardhat Tasks
How to Double-Check Smart Contract State Changes with Hardhat Tasks